a guy wire from the top of the transmission
In data communicating terminology, a transmitting medium is a physical course between the transmitter and the liquidator i.e. it is the television channel through and through which data is dispatched from unitary place to another. Transmission Media is broadly classified into the following types:
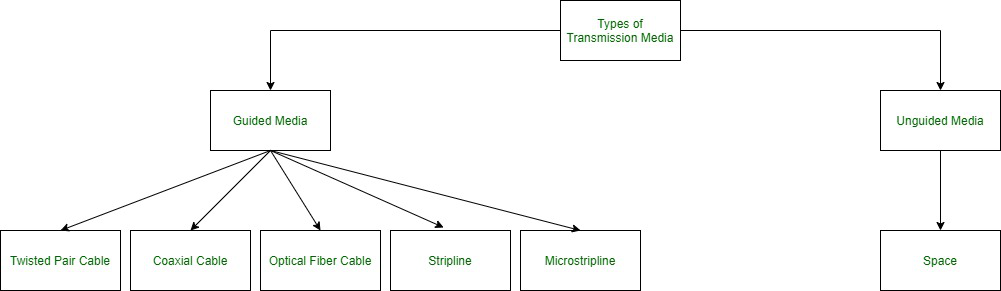
1. Guided Media:
It is also referred to as Wired operating room Bounded transmittal media. Signals organism transmitted are directed and close in a constricting pathway by using physical golf links.
Features:
- High Speed
- Secure
- Used for comparatively shorter distances
There are 3 senior types of Guided Media:
(i) Twisted Pair Telegraph –
IT consists of 2 separately insulated conductor wires injury about each other. Generally, different such pairs are bundled in concert in a protective sheath. They are the most widely used Transmission Media. Twisted Pair is of ii types:
- Unprotected Twisted Pair (UTP):
UTP consists of cardinal insulated copper wires twisted around one another. This type of cable has the ability to block interference and does not reckon on a physical shield for this purpose. It is used for telephonic applications.

Advantages:
⇢ Least dear
⇢ Impressionable to install
⇢ High-f number capacity
⇢ Susceptible to outer interference
⇢ Turn down capacity and performance in comparison to STP
⇢ Short distance transmission due to fading
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP):
This type of cable's length consists of a specialised jacket (a copper gold braid covering Beaver State a foil shield) to draw a blank foreign interference. It is used in red-hot-data-range Ethernet and in phonation and information channels of telephone lines.
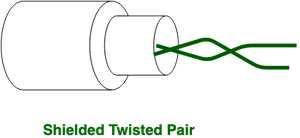
Advantages:
⇢ Better performance at a higher data range in comparison to UTP
⇢ Eliminates XT
⇢ Comparatively quicker
⇢ Relatively defiant to establis and manufacture
⇢ More expensive
⇢ Bulky
(ii) Concentric Cable television –
It has an outer plastic covering containing an insulation layer successful of PVC or Teflon and 2 symmetrical conductors from each one having a separate insulated protection cover. The coax cable transmits entropy in two modes: Baseband mode(dedicated cable system bandwidth) and Broadband mode(cable bandwidth is split into separate ranges). Cable's length TVs and analogue television networks widely usage Coaxial cables.
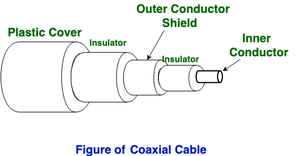
Advantages:
- High Bandwidth
- Better randomness Immunity
- Easy to install and expand
- Inexpensive
Disadvantages:
- Single cable system bankruptcy pot disrupt the whole network
(iii) Optical Fiber Cable –
It uses the construct of reflection of illume through a gist made up of glass or plastic. The marrow is surrounded by a little dense glass or plastic covering called the cladding. It is ill-used for the transmission of large volumes of data.
The cable can be unidirectional or biface. The WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer) supports two modes, that is to say unidirectional and bidirectional mode.
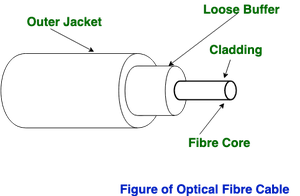
Advantages:
- Increased capacity and bandwidth
- Lightweight
- Less signalize attenuation
- Unsusceptibility to electromagnetic interference
- Resistance to corrosive materials
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to set u and hold over
- High cost
- Fragile
(quaternity) Stripline
Stripline is a transverse electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium unreal by Robert M. Barrett of the Air Impel Cambridge Research Centre in the 1950s. Stripline is the earliest class of the planar transmission line. It uses a conducting material to transmit up-frequency waves it is also known as a waveguide. This conducting material is sandwiched between two layers of the solid ground plane which are usually shorted to provide EMI immunity.
(v) Microstripline
In that, the conducting material is separated from the establish plane by a layer of dielectric.
2. Unguided Media:
It is also referred to as Wireless surgery Unbounded transmission media. No physical medium is required for the transmission of electromagnetic signals.
Features:
- The indicate is broadcasted through publicise
- Less Secure
- Used for larger distances
There are 3 types of Signals sent through with unguided media:
(i) Radio waves –
These are easy to generate and can penetrate through buildings. The sending and receiving antennas need not personify aligned. Frequency Range:3KHz – 1GHz. AM and FM radios and cordless phones use Radio waves for transmission system.
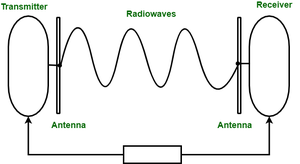
Far Categorized as (i) Terrestrial and (deuce) Artificial satellite.
(two) Microwaves –
IT is a line of visual sense transmission i.e. the sending and receiving antennas need to be properly aligned with all other. The distance covered by the betoken is directly proportional to the height of the antenna. Frequency Range:1GHz – 300GHz. These are majorly used for cell communication and television distribution.

(iii) Unseeable –
Infrared emission waves are used for very fugitive distance communication. They cannot penetrate through obstacles. This prevents interference between systems. Frequency Range:300GHz – 400THz. Information technology is in use in TV remotes, wireless mouse, keyboard, printer, etc.
a guy wire from the top of the transmission
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/types-transmission-media/
Posting Komentar untuk "a guy wire from the top of the transmission"